A Deeper Exploration into Animal Rights and Ethics
This article delves into the complexities of animal rights and ethics, examining philosophical perspectives, legal frameworks, and the societal implications of how we treat non-human animals. In a world where the treatment of animals often raises heated debates, understanding the ethical considerations is crucial. Are we merely stewards of the earth, or do we hold a deeper responsibility towards our fellow creatures? This exploration aims to shed light on these pressing questions.
When we talk about animal rights, we must first consider the philosophical arguments that have shaped this discourse. Thinkers like Peter Singer and Tom Regan have been instrumental in framing the ethical treatment of animals. Singer, in his book "Animal Liberation," argues for the principle of equal consideration of interests, suggesting that the capacity to suffer should be the basis for how we treat all beings, not just humans. On the other hand, Regan posits that animals have inherent value and deserve rights simply because they are sentient beings.
These philosophical foundations challenge us to rethink our relationship with animals. Are they mere resources for human use, or do they have their own rights that deserve protection? This fundamental question invites us to reflect on our moral obligations. It’s like standing at a crossroads; one path leads to exploitation, while the other leads to compassion. Which path will we choose?
Across the globe, various legal frameworks aim to protect animal rights, though the effectiveness and scope of these laws vary significantly. In countries like Germany, animals are recognized as beings with feelings, leading to stringent animal welfare laws. Conversely, in many parts of the world, animals are still viewed primarily as property, lacking any legal rights.
Here’s a brief overview of some significant laws:
| Country | Key Legislation |
|---|---|
| United States | Animal Welfare Act |
| United Kingdom | Animal Welfare Act 2006 |
| Germany | Animal Protection Law |
| India | Prevention of Cruelty to Animals Act |
These laws represent a step towards recognizing animals as more than just property. However, the challenge remains in enforcing these laws and ensuring that they translate into real protections for animals. It’s a bit like having a beautiful map without a reliable compass; the direction is clear, but the journey is fraught with obstacles.
Animal welfare organizations play a pivotal role in advocating for animal rights. Groups like the World Animal Protection and the Humane Society work tirelessly to promote ethical treatment and raise awareness about animal suffering. Their campaigns often highlight the plight of animals in factory farms, laboratories, and entertainment industries.
However, these organizations face numerous challenges, including limited funding, legislative barriers, and societal apathy. It’s akin to David versus Goliath; they are fighting against powerful industries that profit from animal exploitation. Yet, their efforts have led to significant changes, such as the banning of certain cruel practices in various countries.
Public attitudes towards animal rights have evolved dramatically over the past few decades. Once considered fringe, the movement has gained mainstream traction, influenced by cultural shifts, social media, and increased awareness of animal welfare issues. Many people now view animals as companions rather than commodities, leading to a growing demand for ethical products and practices.
This change in perception is crucial. It’s like turning a ship; it takes time and effort, but once it’s moving in a new direction, the impact can be profound. As more individuals adopt veganism or support cruelty-free brands, the ripple effect encourages businesses to rethink their practices.
One of the most contentious issues in the animal rights debate is factory farming. These industrialized systems prioritize profit over the welfare of animals, leading to overcrowded conditions, lack of natural behavior, and inhumane treatment. The ethical implications are staggering. Are we willing to turn a blind eye to the suffering of sentient beings for the sake of convenience and cost?
Critics argue that factory farming not only harms animals but also has devastating environmental impacts. The excessive use of resources and pollution generated by these systems pose serious threats to our planet. It’s a classic case of short-term gain versus long-term sustainability; the question remains, what kind of world do we want to leave for future generations?
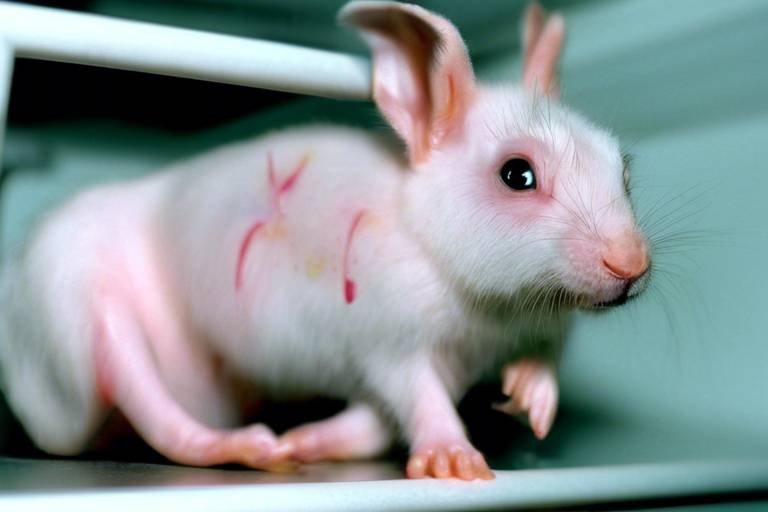
Animal testing is another area rife with ethical dilemmas. While it has historically been justified in the name of scientific progress, the question arises: at what cost? The suffering inflicted on animals in laboratories often goes unnoticed, raising concerns about the morality of using sentient beings for human benefit.
Fortunately, advancements in technology are paving the way for alternatives to animal testing, such as in vitro methods and computer modeling. These innovations not only promise to reduce animal suffering but also improve the reliability of scientific outcomes. It’s like finding a new route on a familiar journey; it may take time to adjust, but the destination can be reached with less harm.
The rise of veganism represents a significant shift in how society views animal rights. More people are recognizing the ethical implications of consuming animal products and are choosing plant-based diets as a way to align their values with their actions. This movement is not only about diet; it encompasses a broader philosophy of compassion and sustainability.
As veganism gains momentum, it challenges industries to adapt. It’s akin to a wave crashing against the shore; it may take time, but the impact is undeniable. The growing demand for vegan products is reshaping markets and encouraging ethical practices.
Looking ahead, the future of animal rights advocacy is promising yet challenging. Emerging trends, such as the use of technology in promoting ethical treatment, are gaining traction. From apps that track animal welfare to virtual reality experiences that educate the public about animal suffering, innovation is becoming a powerful ally in this fight.
Furthermore, potential legal reforms could strengthen protections for animals. As society continues to evolve, so too must our laws and ethical standards. The journey toward a more compassionate world is ongoing, but with each step, we move closer to a reality where animals are treated with the respect they deserve.
- What are animal rights? Animal rights refer to the belief that non-human animals have intrinsic rights, similar to human rights, which protect them from exploitation and harm.
- Why is animal welfare important? Animal welfare is crucial because it reflects our ethical obligations to treat sentient beings with compassion and respect.
- How can I help promote animal rights? You can promote animal rights by supporting animal welfare organizations, choosing cruelty-free products, and adopting a plant-based diet.
- What is the impact of factory farming? Factory farming has significant ethical and environmental implications, including animal suffering, resource depletion, and pollution.

The Philosophical Foundations of Animal Rights
When we dive into the philosophical foundations of animal rights, we find ourselves in a rich tapestry of ideas woven by thinkers throughout history. From ancient philosophies to modern ethical theories, the question of how we should treat non-human animals has sparked intense debate. At the heart of this discourse lies a fundamental inquiry: Do animals possess rights similar to those of humans? This question has led to various interpretations and frameworks that seek to justify the moral consideration of animals.
One of the pivotal figures in this discussion is Peter Singer, whose book Animal Liberation has become a cornerstone of animal rights philosophy. Singer argues from a utilitarian perspective, emphasizing that the capacity to suffer is what grants animals moral consideration. He posits that if a being can experience pain, it deserves to have its interests taken into account, regardless of species. This view challenges traditional anthropocentrism, which places human interests above all else, urging us to expand our moral circle to include all sentient beings.
Another critical thinker is Tom Regan, who presents a rights-based approach in his work The Case for Animal Rights. Regan argues that animals are "subjects-of-a-life," possessing inherent value and rights simply by being alive. He believes that animals should not be treated merely as means to human ends, but rather as beings with their own interests and rights. Regan's philosophy invites us to reconsider our legal and moral frameworks, pushing for a recognition of animal rights that parallels human rights.
In addition to Singer and Regan, the animal rights movement has been influenced by various philosophical traditions, including deontology and virtue ethics. Deontological ethics, as proposed by thinkers like Immanuel Kant, emphasizes the importance of duty and moral rules. While Kant himself did not advocate for animal rights, his ideas have inspired others to consider the moral obligations humans have towards animals. On the other hand, virtue ethics, rooted in the works of Aristotle, focuses on the character and virtues of individuals, suggesting that a compassionate and just person would naturally extend kindness to animals.
As we explore these philosophical foundations, it's essential to recognize the interconnectedness of ethics and society. The way we perceive and treat animals reflects our broader values and ethical beliefs. For instance, cultures that emphasize harmony with nature often have more profound respect for animal life, while industrialized societies may prioritize economic gain over ethical considerations. This divergence raises critical questions about the implications of our choices and the moral responsibilities we hold.
In conclusion, the philosophical foundations of animal rights are multifaceted and deeply rooted in ethical inquiry. As we navigate this complex landscape, we must continually challenge our assumptions and strive for a more humane world where animals are treated with the dignity they deserve. The evolution of thought around animal rights not only shapes our treatment of animals but also reflects our growth as a society. By engaging with these philosophical perspectives, we can foster a deeper understanding of our ethical obligations and work towards a more compassionate future.
- What is the main argument for animal rights? The primary argument for animal rights revolves around the idea that animals deserve moral consideration due to their capacity to suffer and have interests.
- Who are the key philosophers in the animal rights movement? Key philosophers include Peter Singer, who advocates for a utilitarian approach, and Tom Regan, who argues for a rights-based perspective.
- How do cultural attitudes affect animal rights? Cultural attitudes significantly influence how societies view and treat animals, with some cultures emphasizing harmony with nature and others prioritizing economic interests.

Legal Frameworks Protecting Animal Rights
When we think about animal rights, it’s essential to look at the legal frameworks that exist to protect these rights. Across the globe, various laws and regulations have been established to ensure that non-human animals receive a certain level of protection from harm and exploitation. However, the effectiveness and enforcement of these laws can vary significantly from one country to another, creating a complex landscape of animal welfare legislation.
In many countries, animal welfare laws are often rooted in the recognition of animals as sentient beings capable of experiencing pain and suffering. This shift in perception has paved the way for significant legal reforms. For example, in the European Union, the Treaty of Amsterdam recognized animals as sentient beings, leading to stricter regulations regarding their treatment. This includes directives that govern the conditions in which animals are kept, transported, and slaughtered.
In the United States, the Animal Welfare Act (AWA) is a pivotal piece of legislation that sets the minimum standards for the treatment of animals in research, exhibition, transport, and by dealers. However, it’s important to note that the AWA does not cover all animals—most notably, it excludes farm animals and animals used for food production. This gap in legislation raises significant ethical questions about the treatment of animals in factory farming, where millions of animals are raised under conditions that many consider inhumane.
Moreover, some countries have implemented comprehensive animal rights laws that go beyond welfare and focus on the rights of animals. For instance, in Switzerland, animals are granted legal rights, and the Swiss Federal Constitution explicitly states that animals must be treated with respect and dignity. This legal recognition has led to progressive reforms in animal protection laws, including bans on certain practices deemed cruel.
To illustrate the differences in legal frameworks worldwide, consider the following table that highlights some key animal protection laws in various countries:
| Country | Key Legislation | Focus Area |
|---|---|---|
| United States | Animal Welfare Act (AWA) | Research, exhibition, and transport |
| United Kingdom | Animal Welfare Act 2006 | General welfare of domestic animals |
| Germany | Basic Law for the Protection of Animals | Animal rights as constitutional law |
| Switzerland | Animal Protection Act | Comprehensive animal rights |
Despite these advancements, there are still significant challenges in enforcing animal rights laws. Many countries lack the resources or political will to implement these laws effectively. Additionally, cultural attitudes towards animals can hinder progress; in some societies, animals are still viewed primarily as property, which complicates the legal landscape.
Animal welfare organizations play a crucial role in advocating for stronger legal protections and raising public awareness about animal rights issues. Through campaigns, education, and lobbying efforts, these organizations strive to ensure that animals are treated humanely and that their rights are recognized. However, they often face pushback from industries that rely on animal exploitation, making their mission even more challenging.
As we navigate the intricate web of animal rights legislation, it’s clear that while there have been significant strides forward, there is still much work to be done. The evolution of legal frameworks protecting animal rights will depend on ongoing advocacy, public support, and a commitment to viewing animals not just as resources, but as beings deserving of respect and ethical treatment.
- What is the Animal Welfare Act? The Animal Welfare Act is a U.S. law that sets minimum standards for the treatment of animals in research, exhibition, transport, and by dealers.
- Are all animals protected under animal rights laws? No, many laws do not cover farm animals or animals used for food production, which raises ethical concerns.
- Which countries have the strongest animal rights laws? Countries like Germany and Switzerland have comprehensive legal protections that recognize animals as sentient beings with rights.

The Role of Animal Welfare Organizations
Animal welfare organizations play a crucial role in championing the rights and well-being of animals across the globe. These organizations are not just passive observers; they are active participants in the fight against cruelty and exploitation. They work tirelessly to raise awareness, advocate for stronger legal protections, and provide direct assistance to animals in need. Imagine a world where animals are treated with the respect and dignity they deserve—this vision is what drives many of these organizations.
One of the most significant contributions of animal welfare organizations is their ability to educate the public about animal rights. Through campaigns, workshops, and community outreach, they inform people about the ethical treatment of animals and the importance of compassion. For instance, many organizations conduct school programs that teach children about kindness to animals, fostering a new generation of advocates. This education is essential because it helps shift societal attitudes and encourages individuals to take action.
Moreover, these organizations often engage in legislative advocacy, pushing for laws that protect animals from abuse and exploitation. They monitor legislative developments, lobby policymakers, and mobilize public support for animal-friendly laws. In many cases, they are the driving force behind significant legal reforms. To illustrate, organizations have successfully campaigned for laws banning puppy mills, improving conditions for farm animals, and prohibiting the use of animals in cruel entertainment practices.
In addition to advocacy and education, animal welfare organizations also provide direct services to animals. This includes rescuing abandoned or abused animals, offering shelter and rehabilitation, and facilitating adoptions. Many organizations run animal shelters that serve as safe havens for pets in distress. These shelters not only care for animals but also work to find them loving homes, which is a vital part of the solution to the problem of pet overpopulation.
However, the journey of these organizations is not without challenges. They often face limited funding and resources, which can hinder their ability to carry out their mission effectively. Many rely on donations and grants, which can fluctuate based on economic conditions. Additionally, they may encounter resistance from industries that profit from animal exploitation, such as factory farming and animal testing. This opposition can make it difficult for organizations to achieve their goals and create meaningful change.
Despite these challenges, the impact of animal welfare organizations cannot be overstated. Their relentless efforts have led to increased public awareness and a growing movement towards ethical treatment of animals. As more people become aware of the issues, they are inspired to support these organizations, whether through volunteering, donating, or simply spreading the word. The ripple effect of their work is profound, influencing not only animal welfare policies but also societal norms regarding how we treat non-human animals.
In conclusion, animal welfare organizations are vital to the advancement of animal rights. They educate, advocate, and provide essential services, all while facing significant challenges. Their work is a testament to the power of collective action in creating a more humane world. As we continue to evolve in our understanding of animal ethics, these organizations will undoubtedly remain at the forefront of the movement, pushing for a future where all animals are treated with the respect they deserve.
- What is the main goal of animal welfare organizations?
Animal welfare organizations aim to protect animals from abuse and neglect, promote ethical treatment, and advocate for stronger legal protections. - How can I support animal welfare organizations?
You can support these organizations by volunteering your time, donating funds, or spreading awareness about their missions and campaigns. - What challenges do animal welfare organizations face?
Many organizations struggle with limited funding, public awareness, and opposition from industries that exploit animals.

Public Perception and Animal Rights
Public perception of animal rights has undergone a remarkable transformation over the past few decades. Once viewed as a niche concern, animal rights have now become a significant topic of discussion, influencing everything from legislation to consumer choices. This shift can be attributed to various factors, including increased awareness of animal welfare issues, the rise of social media, and changing cultural attitudes towards animals. Have you ever stopped to consider how your views on animals might differ from those of previous generations? It's fascinating to think about how our understanding of animal sentience and suffering has evolved.
One of the most significant catalysts for change has been the exposure of cruel practices in industries such as factory farming and animal testing. Documentaries, undercover investigations, and viral social media posts have brought these issues to the forefront of public consciousness. People are increasingly questioning the ethics of consuming animal products and supporting industries that exploit animals. This growing awareness has led to a surge in interest in plant-based diets, animal welfare legislation, and ethical consumerism. It's almost like a ripple effect—one act of awareness leads to another, and before you know it, a wave of change is sweeping across society.
To understand the nuances of public perception, it's essential to consider the demographic factors at play. Research shows that younger generations tend to be more empathetic towards animals and are more likely to support animal rights initiatives. For instance, a 2021 survey revealed that:
| Age Group | Support for Animal Rights (%) |
|---|---|
| 18-24 | 78% |
| 25-34 | 72% |
| 35-44 | 65% |
| 45+ | 55% |
This table illustrates a clear trend: as age increases, support for animal rights tends to decrease. This could be due to various reasons, including traditional views on animal use in agriculture and entertainment. However, it's essential to recognize that public perception is not static; it is influenced by education, media exposure, and personal experiences. For example, people who have pets often develop a deeper understanding of animal emotions and behaviors, leading them to advocate for better treatment of all animals.
Moreover, cultural and social factors play a significant role in shaping attitudes towards animal rights. In some cultures, animals are revered and protected, while in others, they are primarily viewed as resources. This disparity can lead to conflicting views on animal rights and welfare. For instance, in countries where eating certain animals is a tradition, advocacy for animal rights may face resistance. However, as globalization spreads ideas and practices, even these traditional views are being challenged. It's a complex web of beliefs and values that continues to evolve.
As public perception shifts, so does the landscape of animal rights advocacy. Organizations are adapting their messaging to resonate with a broader audience. They are using social media platforms to engage younger generations, employing relatable language, and sharing compelling stories that highlight the plight of animals. This modern approach to advocacy is crucial in fostering a culture of empathy and action. But is it enough? Can we truly shift societal norms when long-standing traditions are at play? The answer lies in continued dialogue and education.
In conclusion, public perception of animal rights is a dynamic and multifaceted issue. It is shaped by a myriad of factors, including age, culture, and personal experiences. As we continue to engage in conversations about animal welfare, it's vital to recognize the power of awareness and empathy. After all, the way we treat animals reflects our values as a society. So, what can you do to contribute to this evolving narrative? Whether it's adopting a plant-based diet, supporting animal welfare organizations, or simply educating yourself and others, every action counts.
- What are animal rights? Animal rights refer to the belief that non-human animals are entitled to live free from human exploitation and harm.
- How has public perception changed over time? Public perception has shifted towards greater empathy and support for animal rights, largely influenced by awareness campaigns and changing cultural attitudes.
- What role do social media play in animal rights advocacy? Social media amplifies awareness of animal welfare issues, allowing organizations to reach a broader audience and engage in meaningful conversations.
- Are younger people more supportive of animal rights? Yes, studies indicate that younger generations tend to be more supportive of animal rights compared to older generations.

Factory Farming and Its Ethical Implications
Factory farming is a term that evokes a myriad of emotions and ethical dilemmas. At its core, it represents a system of agriculture that prioritizes efficiency and profit over the well-being of animals. Imagine a world where animals are treated as mere commodities, crammed into overcrowded spaces, deprived of natural behaviors, and subjected to inhumane conditions. This is the stark reality of factory farming, and it raises profound questions about our moral obligations toward non-human animals.
One of the most pressing ethical implications of factory farming is the sheer scale of suffering inflicted on animals. Chickens, pigs, and cows are often raised in environments that are not only cramped but also devoid of proper care and attention. For instance, a typical broiler chicken may live its entire life in a space no larger than a sheet of paper, leading to severe physical and psychological stress. Is it justifiable to prioritize economic gain over the welfare of sentient beings? This question lingers in the minds of many as they grapple with the realities of modern agriculture.
Moreover, the environmental consequences of factory farming cannot be overlooked. The intensive farming practices contribute significantly to pollution, deforestation, and greenhouse gas emissions. For example, a report from the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) highlights that livestock production is responsible for approximately 14.5% of global greenhouse gas emissions. This not only endangers animal welfare but also poses a threat to our planet's health. The ethical implications extend beyond the animals themselves, impacting ecosystems and future generations.
To illustrate the contrast between traditional farming practices and factory farming, consider the following table:
| Aspect | Traditional Farming | Factory Farming |
|---|---|---|
| Animal Space | Ample space for movement | Cramped, overcrowded conditions |
| Animal Welfare | Focus on humane treatment | Profit-driven, often neglectful |
| Environmental Impact | Lower emissions, sustainable | High emissions, pollution |
As consumers become more aware of these ethical implications, there is a growing call for transparency in food production. Many people now seek out labels that signify humane treatment and sustainable practices. This shift in consumer behavior is a powerful tool for change, as it encourages producers to adopt more ethical practices. Can our choices at the grocery store really make a difference? Absolutely! Every purchase is a vote for the kind of agriculture we want to support.
In conclusion, the ethical implications of factory farming are vast and complex. From animal suffering to environmental degradation, the consequences of prioritizing profit over compassion are felt across multiple facets of our society. As we navigate this challenging landscape, it’s crucial to stay informed and advocate for practices that respect both animal welfare and our planet. As consumers, we hold the power to influence change, one meal at a time.
- What is factory farming? Factory farming refers to the industrialized production of livestock, where animals are raised in confined spaces and often subjected to inhumane conditions.
- How does factory farming affect animal welfare? Animals in factory farms typically experience overcrowding, lack of natural behaviors, and poor living conditions, leading to significant suffering.
- What are the environmental impacts of factory farming? Factory farming contributes to pollution, deforestation, and greenhouse gas emissions, which adversely affect the environment.
- How can consumers make a difference? By choosing products that are labeled as humane or sustainable, consumers can support better practices in agriculture.

Animal Testing: Ethical Dilemmas
Animal testing has long been a contentious issue, sparking heated debates among ethicists, scientists, and the general public. At its core, the ethical dilemmas surrounding animal testing hinge on a fundamental question: Is it justifiable to use animals for the sake of human advancement? This question not only challenges our moral compass but also forces us to confront the implications of our choices. On one hand, proponents argue that animal testing is essential for medical breakthroughs and safety assessments, while on the other hand, critics highlight the suffering inflicted on sentient beings and advocate for alternative methods.
To understand the complexities, we need to consider the various arguments that populate this debate. Supporters of animal testing often cite the historical context, noting that many life-saving treatments and vaccines have emerged from research involving animals. For instance, the development of insulin and the polio vaccine are often heralded as triumphs achieved through animal research. However, this perspective raises an important counterpoint: At what cost do these advancements come? The ethical implications of causing pain, distress, and even death to animals cannot be overlooked.
Moreover, the scientific validity of animal testing is increasingly under scrutiny. Critics argue that results obtained from animal models do not always translate effectively to humans due to physiological differences. As a result, many researchers are advocating for a shift towards more humane and scientifically sound alternatives. These include in vitro testing, computer modeling, and the use of human cell cultures, which can provide more relevant data without the ethical baggage of animal suffering.
In light of these dilemmas, several organizations and regulatory bodies have begun to implement guidelines that aim to minimize animal suffering. The 3Rs principle—Replacement, Reduction, and Refinement—has become a guiding framework in many research institutions. This principle encourages scientists to seek alternatives to animal testing, reduce the number of animals used, and refine procedures to lessen pain and distress. However, the effectiveness of these guidelines often depends on the commitment of researchers and the availability of funding for alternative methods.
As society becomes more aware of animal rights and welfare, the conversation around animal testing is evolving. Many consumers are now demanding transparency and ethical considerations in the products they use. This shift in public perception is prompting companies to seek cruelty-free alternatives, leading to a burgeoning market for products that do not involve animal testing. In this context, the ethical dilemmas surrounding animal testing are not just academic; they are increasingly relevant to everyday choices.
Ultimately, the ethical dilemmas of animal testing compel us to reflect on our values and priorities as a society. It challenges us to balance the pursuit of knowledge and innovation with the moral obligation to protect those who cannot speak for themselves. As we navigate this complex landscape, it is essential to remain open to dialogue, to consider the perspectives of all stakeholders, and to strive for solutions that respect both human and animal welfare.
- What is animal testing? Animal testing refers to the use of non-human animals in experiments to assess the safety and efficacy of products, primarily in the fields of medicine and cosmetics.
- Why is animal testing controversial? It is controversial because it raises ethical concerns about the treatment of animals, the validity of results, and the necessity of using animals for human benefits.
- What are the alternatives to animal testing? Alternatives include in vitro testing, computer simulations, and advanced cell culture techniques that do not involve the use of live animals.
- How can I support animal rights? You can support animal rights by advocating for legislation that protects animals, choosing cruelty-free products, and educating others about the importance of ethical treatment of animals.

Impact of Veganism on Animal Rights
Veganism has emerged as a significant movement that not only promotes a plant-based diet but also serves as a powerful advocate for animal rights. At its core, veganism challenges the traditional views of how we interact with animals, pushing society to reconsider the ethical implications of consuming animal products. But what does this shift really mean for animal rights? Let’s dive deeper into the impact of veganism on the landscape of animal welfare.
One of the most profound effects of the vegan movement is its ability to raise awareness about the plight of animals in various industries. As more people adopt vegan lifestyles, they often become more informed about the conditions in which animals are raised, transported, and slaughtered. This newfound awareness can lead to a ripple effect, encouraging individuals to advocate for better treatment of animals and to support legislation aimed at improving animal welfare.
Moreover, the rise of veganism has sparked significant changes in consumer behavior. As demand for plant-based alternatives grows, many companies are responding by developing new products that cater to this market. This shift not only provides more options for consumers but also puts pressure on industries that rely on animal products to reconsider their practices. For instance, veganism has led to a noticeable decline in the consumption of meat and dairy products in some regions, which in turn affects the factory farming industry, a major contributor to animal suffering.
Additionally, the ethical arguments presented by vegans often highlight the intrinsic value of non-human animals. By emphasizing that animals are capable of feeling pain, joy, and suffering, vegan advocates challenge the notion that animals are merely resources for human use. This philosophical shift is crucial in promoting animal rights, as it encourages society to view animals as sentient beings deserving of respect and compassion.
Veganism also intersects with environmental concerns, further bolstering the argument for animal rights. The environmental impact of animal agriculture is staggering, contributing to deforestation, greenhouse gas emissions, and loss of biodiversity. By opting for a vegan lifestyle, individuals are not only taking a stand for animal welfare but are also making a choice that benefits the planet. This dual focus on ethical treatment and environmental sustainability can unite various advocacy groups, creating a more robust movement for change.
However, the vegan movement is not without its challenges. Despite the growing popularity of plant-based diets, misconceptions and resistance still exist. Some people argue that veganism is impractical or too expensive, while others may feel threatened by the idea of changing long-standing dietary habits. Addressing these perceptions is crucial for the continued growth of veganism and its impact on animal rights.
In conclusion, the rise of veganism is reshaping discussions around animal rights in profound ways. By promoting awareness, influencing consumer behavior, and advocating for ethical treatment, veganism plays a pivotal role in the broader animal rights movement. As society continues to grapple with these complex issues, the conversation around veganism and animal rights will undoubtedly evolve, paving the way for a future where animals are treated with the respect they deserve.
- What is veganism? Veganism is a lifestyle choice that excludes all animal products, including meat, dairy, and eggs, in order to promote animal rights and environmental sustainability.
- How does veganism impact animal rights? Veganism raises awareness about animal suffering, influences consumer behavior, and advocates for ethical treatment of animals.
- Are there health benefits to being vegan? Many studies suggest that a well-planned vegan diet can provide health benefits, including lower risks of certain diseases.
- Can veganism help the environment? Yes, by reducing reliance on animal agriculture, veganism can contribute to lower greenhouse gas emissions and less environmental degradation.

Future Directions in Animal Rights Advocacy
The future of animal rights advocacy is poised for significant transformation, driven by a confluence of social awareness, technological advancements, and legal reforms. As we move forward, the dialogue surrounding animal rights is becoming increasingly complex and nuanced, reflecting a growing recognition of the intrinsic value of non-human animals. This shift is not merely a trend; it represents a fundamental change in how society perceives and interacts with the animal kingdom.
One of the most promising directions in animal rights advocacy is the integration of technology into efforts to promote ethical treatment. Innovations such as artificial intelligence and virtual reality are being harnessed to create more effective campaigns and educational tools that raise awareness about animal welfare. For instance, virtual reality experiences can immerse individuals in the lives of animals, fostering empathy and understanding in ways traditional media cannot. This technology-driven approach is particularly appealing to younger generations, who are increasingly engaged with digital platforms.
Moreover, the rise of social media has revolutionized how advocacy groups communicate and mobilize support. Platforms like Instagram and TikTok allow organizations to reach a broader audience, share impactful stories, and rally grassroots movements. This digital activism is not just about spreading awareness; it’s about creating a community of advocates who can collectively push for change. The viral nature of social media campaigns can lead to significant shifts in public opinion, making it a powerful tool in the fight for animal rights.
Another critical area of focus for future advocacy is legal reform. As public sentiment towards animal welfare continues to evolve, there is a growing push for more comprehensive legislation that protects animals from cruelty and exploitation. This includes not only stricter regulations on factory farming and animal testing but also the recognition of animals as sentient beings deserving of legal rights. Countries like New Zealand and Switzerland are already leading the way with progressive laws, and there is hope that these examples will inspire similar reforms worldwide.
In addition, the global movement towards veganism and plant-based diets is reshaping discussions around animal rights. As more people adopt these lifestyles, the demand for ethical and sustainable food sources grows, prompting food industries to adapt. This shift not only benefits animals but also has profound implications for environmental sustainability. Advocacy groups are increasingly focusing on the interconnectedness of animal rights and environmental issues, highlighting how ethical treatment of animals can contribute to a healthier planet.
However, the road ahead is not without challenges. Advocacy groups must navigate a landscape filled with opposing interests, from agricultural industries to pharmaceutical companies. The ethical dilemmas surrounding animal testing and factory farming are deeply entrenched in economic systems that prioritize profit over welfare. To combat these obstacles, collaboration among various stakeholders—such as scientists, policymakers, and activists—will be essential. Only through a united front can animal rights advocates hope to effect meaningful change.
In conclusion, the future of animal rights advocacy is bright but requires persistent effort and innovation. By leveraging technology, engaging in legal reforms, and promoting sustainable practices, advocates can continue to push the envelope on animal welfare. As society becomes more aware of the ethical implications of our treatment of animals, the potential for change grows exponentially. The journey towards a more compassionate world for all living beings is just beginning, and every voice matters in this critical conversation.
- What are the main goals of animal rights advocacy? The primary goals include ending animal cruelty, promoting ethical treatment, and establishing legal rights for animals.
- How can technology aid animal rights advocacy? Technology can enhance awareness through virtual experiences and social media campaigns, making advocacy more engaging and impactful.
- What role does veganism play in animal rights? Veganism promotes a lifestyle that avoids animal exploitation, directly supporting the mission of animal rights advocacy.
- Are there any countries leading in animal rights legislation? Yes, countries like New Zealand and Switzerland are recognized for their progressive animal welfare laws.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What are the main philosophical arguments for animal rights?
The philosophical arguments for animal rights often revolve around the idea of sentience, which suggests that if animals can experience pain and pleasure, they deserve moral consideration. Thinkers like Peter Singer advocate for utilitarianism, arguing that we should minimize suffering for all sentient beings, while Tom Regan emphasizes the inherent value of animals, asserting they have rights similar to human rights.
- How do legal frameworks protect animal rights?
Legal frameworks for animal rights vary widely across countries. In some places, there are comprehensive laws that prohibit cruelty and ensure welfare standards, while in others, protections are minimal or non-existent. Key legislation includes the Animal Welfare Act in the U.S. and the Animal Protection Act in various European nations, which aim to safeguard animals from abuse and exploitation.
- What role do animal welfare organizations play?
Animal welfare organizations play a crucial role in advocating for the rights of animals. They engage in campaigns to raise awareness, lobby for stronger laws, and rescue animals from abusive situations. However, they often face challenges such as limited funding and opposition from industries that exploit animals, making their work both vital and difficult.
- How has public perception of animal rights changed over time?
Public perception of animal rights has evolved significantly, influenced by cultural shifts, media coverage, and increased awareness of animal welfare issues. In recent years, more people are recognizing the ethical implications of animal treatment, leading to a rise in vegetarianism and veganism as individuals seek to align their diets with their values.
- What are the ethical concerns surrounding factory farming?
Factory farming raises serious ethical concerns regarding the treatment of animals. Issues include overcrowding, inhumane living conditions, and practices that prioritize profit over animal welfare. Additionally, the environmental impact of these operations, such as pollution and resource depletion, adds another layer of ethical consideration that society must address.
- What are the dilemmas associated with animal testing?
Animal testing is a contentious issue, with ethical dilemmas stemming from the conflict between scientific advancement and animal welfare. Proponents argue that it is necessary for medical breakthroughs, while opponents highlight the suffering inflicted on animals and advocate for alternative methods. The ongoing debate calls for a balance between innovation and ethical responsibility.
- How does veganism impact animal rights discussions?
The rise of veganism has significantly reshaped discussions around animal rights, promoting a lifestyle that seeks to eliminate animal exploitation. This movement not only addresses ethical concerns but also highlights environmental and health implications, encouraging a broader conversation about sustainable living and compassionate choices.
- What is the future of animal rights advocacy?
The future of animal rights advocacy looks promising with emerging trends such as increased public awareness, potential legal reforms, and the integration of technology in promoting animal welfare. As society continues to evolve, the advocacy landscape will likely adapt, focusing on innovative solutions and stronger protections for non-human animals.